Time of Flight Techniques
Contact
- LANSCE User Program
- (505) 667-6797
Neutron Time-of-Flight
Since the LANSCE proton beam is pulsed, the energy of the neutrons that are produced can be determined by time-of-flight (TOF) techniques. The proton beam pulse strikes the tungsten neutron production target and neutrons, gamma rays, and charged particles are produced. The charged particles are removed from the beam by permanent magnets. The neutrons and gamma rays travel the distance of the flight path to arrive at a sample or detector. Because gamma rays travel at the speed of light, the gamma rays arrive first. As the neutrons traverse the flight path distance, the neutron pulse becomes broader with the highest energy neutrons arriving before the lower energy neutrons. A measurement of the time between the proton beam pulse and the detection of a signal from the detector gives the velocity or the energy of the neutron.
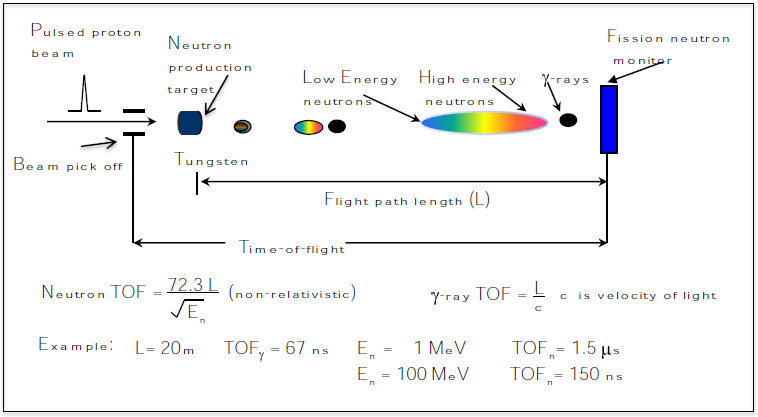
Time-of-flight technique
Depending on the micropulse spacing, gamma rays and high-energy neutrons produced by the following proton pulse will arrive at the same time as low-energy neutrons. This is called "wrap around" and sets a lower limit for the neutron energy that can be used in an experiment. One contribution to the incident neutron energy resolution in a TOF experiment is the time resolution of the detector system. The energy resolution is given by ΔE/E= 2 ΔT/T, where ΔE is the neutron energy resolution, ΔT is the time resolution of the detector, and T is the TOF of the neutron. Table 1 gives values for neutron and gamma ray TOF, wrap-around energy for 1.8 μs and 3.6 μs spacing and energy resolution for various flight path lengths assuming 1 ns detector time resolution.
Table 1
| Flight Path Length (m) | Neutron Energy (MeV) | TOF-γ (ns) | TOF n (ns) | Wrap Around 1.8 μs (keV) | Wrap Around 3.6 μs (keV) | ΔE (keV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1 | 33 | 722 | 161.34 | 40.33 | 3 |
| 2 | 511 | 8 | ||||
| 10 | 230 | 87 | ||||
| 20 | 164 | 244 | ||||
| 100 | 78 | 2569 | ||||
| 500 | 44 | 22739 | ||||
| 20 | 1 | 67 | 1445 | 645.34 | 161.34 | 1 |
| 2 | 1023 | 4 | ||||
| 10 | 460 | 43 | ||||
| 20 | 328 | 122 | ||||
| 100 | 156 | 1285 | ||||
| 500 | 88 | 11369 | ||||
| 90 | 1 | 300 | 6502 | 13068.23 | 3267.06 | 0 |
| 2 | 4601 | 1 | ||||
| 10 | 2071 | 10 | ||||
| 20 | 1476 | 27 | ||||
| 100 | 701 | 285 | ||||
| 500 | 396 | 2527 |

